Cisco Guest Wi-Fi Traffic Tunneling
Guest Wi-Fi is network connections provided by firms to their guests to gain access to the Internet without compromising the security of the host enterprise by using the guest Wi-Fi traffic tunneling technique.
Wi-Fi guest access these days is expected to be available for guests in almost every location, be it in a hospital, at airports, or a company that you visit for an interview.
Guests using the corporate networks to access the internet would compromise the security of the firm as they could sniff the packets, listen to conversations, and access internal resources if not isolated properly. Traditionally, guests have just used a separate SSID and a dedicated VLAN for path isolation, but the “one size fits all” approach does not meet the requirements for flexible and secure guest access.
Cisco recommends using a dedicated controller for guest access which is known as an Anchor controller to achieve guest Wi-Fi traffic tunneling.
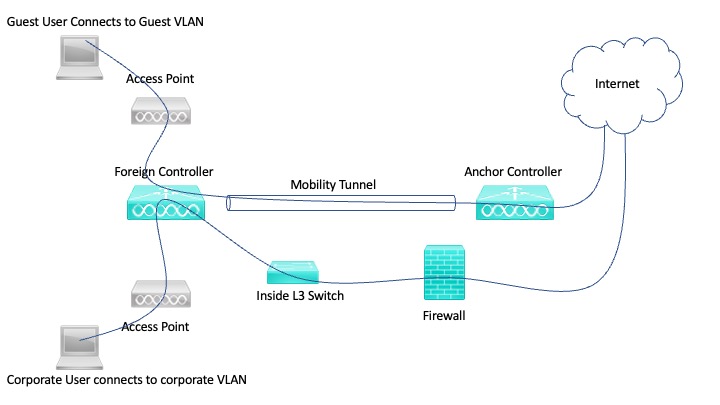
Guest users initially connect to the internal controller also known as a foreign controller which is the point of attachment (POA) and then tunnels the traffic to a controller which is placed in the DMZ zone also known as the anchor controller which is the point of presence for the guest client. This feature restricts a WLAN (Guest WLAN in this case) to a single subnet, regardless of a client entry point into the network.
Packets from the client are encapsulated and sent through the tunnel to the anchor wireless LAN controller.
The anchor controller de-encapsulates the client packets and delivers them to the internet in this case and the return traffic to the client also goes through the same tunnel
This way we achieve complete path isolation for guest network traffic.
Configuration Guide
Wireless Mobility Verification and Troubleshooting commands
AirOS Commands
Show Commands
show mobility summary
show mobility statistics
Show mobility dtls connection
Debug Commands
debug mobility keep-alive enable
debug mobility error enable
debug mobility handoff enable
debug mobility dtls error enable
debug mobility dtls event enable
9800 WLC commands
Show Commands
Show wireless management trustpoint
Show wireless mobility summary
Show wireless mobility peer ip <client IP address>
Show tech-support wireless mobility
Show wireless stats mobility messages
Show wireless stats mobility dtls
Debug Commands
debug client <mac_address in format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx>
debug mobility handoff enable
Enable RA Trace
Reference
Reference 1: http://revolutionwifi.blogspot.com/2010/10/auto-anchor-mobility-fundamentals.html



Nice documentation – thanks for simplifying the concept