Network vs Application Centric

Network vs application-centric is the key design topic whenever you plan for Cisco’s ACI. However, most of the adopters are not very clear about the use cases. The following questions were asked.
- Does ACI automatically capture the application details? also, does it identifies my applications?
- Can ACI automate the application connectivity configurations!
- What is the additional licensing required for application-centric design?
Obviously, the answer to all the above questions is “NO”. Also, I end up clarifying customers on how ACI can be used for doing the policy for their application. Which definitely is one of the differentiators with other SDN solutions. ACI configurations are policy-oriented and when it comes to the policy constructs. On ACI you can use three different methods.
- Network-Centric Approach
- Application-centric approaches.
- Or a combination of network and application-centric
Application Centric Approach
Cisco ACI application network profile (ANP) policy on the APIC controller represents the application, related tiers, and security requirements. The example below shows how a typical three-tier Whatsapp application would be set up with its EPGs( Endpoint Groups). For example, for Whatsapp ANP, it could have EPGs such as WhatsApp’s WEB servers, APP servers, DB servers, etc, and its provider and consumer contracts.
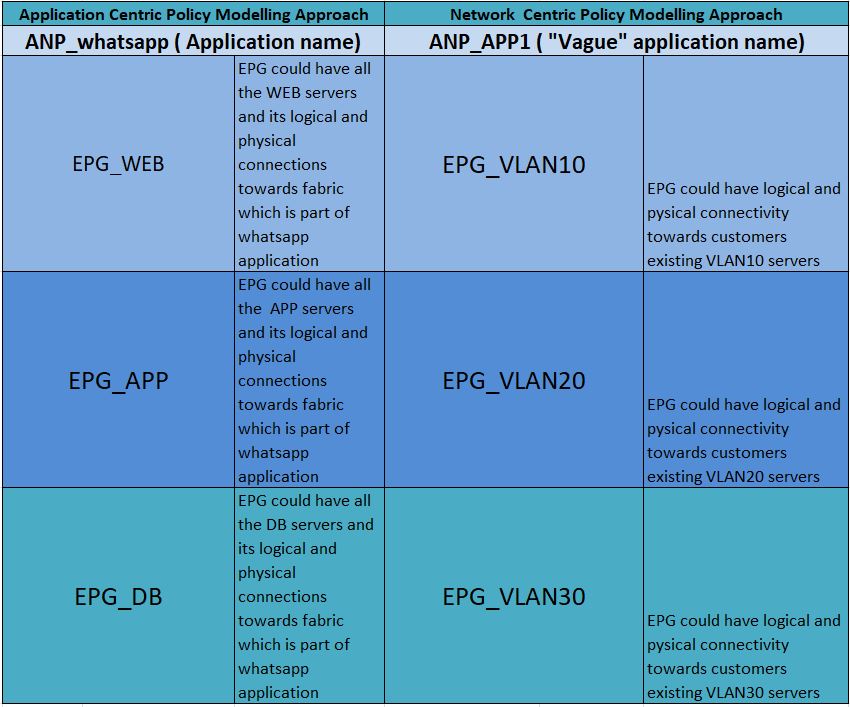
In short, the approach is called application-centric if the policies are created based on application details such as required port-for communication between the tiers, etc. The idea is to give the network administrator a view of the application, its connectivity & security requirements from the ACI controller.
Furthermore for creating ANP, the key requirement is to have the application visibility and its dependencies. If you have Cisco Tetration, it is one of the solutions which could help you to get visibility and application dependency mapping ( ADM) into each of the flows.
Network-Centric Approach
On the other hand, Network-centric uses the constructs like VLANs and subnets. The network-centric is the preferred approach for legacy migration scenarios. This could ensure that during applications migration unknown traffic types are not blocked. In the Network-centric approach the EPG mapping will be equivalent to the following:
- ACI EPG-A mapped to VLAN 10
- ACI EPG-B mapped to VLAN 20
For instance, the above mapping represents that the connectivity of the servers under VLANs mapped to corresponding EPG’s. furthermore, different EPG endpoints traffic can be controlled using contracts. Clearly, doing a network-centric approach is the easiest way to model the policies. of course, here the key requirement is to have the customers VLAN and related connectivity details
Combination of Network & Application Centric
Depends on the use cases, you can also combine the network & application-centric model. Usually, the newly deployed applications could make use of application-centric and the exiting application can be done using network-centric. In addition, it is also possible to migrate from the network to the application-centric model. However, it requires careful planning as the VLAN, subnetting details on the server-side may require modification. Above all, as stated earlier, it requires, ADM to formulate required security policies
Recommendation
- If there is an option to use Tetration or any other ADM tool use them to create an application profile on ACI
- If the above is not an option – make it as simple as VLAN to EPG mapping
Conclusion
So it is not a question of network vs application-centric. Clearly, “application-centric” is a design approach, which heavily depends on the ADM. Additionally, proper profiling of it may require re-designing of server-side connectivity. However, no additional features or advance licensing is required.
Finally, for further reading please refer the following link: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/data-center-virtualization/application-centric-infrastructure/white-paper-c11-737361.html
Also don’t forget to read the feature and benefits of ACI. Happy Learning.
Good day, Thank you for this article my question is related to a brown fields install where we have a network centric network and needs to move to Application but the servers are all hosted on the same subnet /24. If I created a EPG I need to bind this to the BD and Vrf . Will I then created Web-EPG , APP-EPG and DB-EPG and map all of them to the same BD which points to the the /24 subnet? Or how would I accomplish this maybe using TAGS?
Hi jcv365 – thank of your question. I don’t recommend going for mapping your application tiers to single BD – as the BD is equivalent to a broadcast domain. the best way is to group is your application functions into corresponding EPG/VLAN tag and profile them into one ANP. in your case you need to consider re-subnetting of your /24 multiple chunks according to ur application needs.
I hope it answers your queries.
Muhammad Thanks for this article, My question is by adopting network centric approach do we see any changes in traffic flow as compare to Application centric method ? as per my understanding with network centric approach we define EPG based on Vlan or subnet and we only pass traffic between different EPGs based on layer 3 boundaries/known ports (by defining in contracts), as EPG based on subnet or Vlan so we can’t add different subnet device in EPG . Apart from that there is no difference in Network Centric or Application Centric method traffic flow
Hi Sourabh, if you look at it from a traffic flow perspective usually no difference as the flow design usually based on security requirements – you may send traffic through a firewall or other L4L7 devices independent of whether you do network or application-centric.
regards, MM