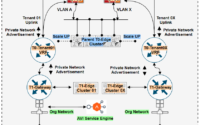
NSX-T Based DMZ Rack Design for Banking
Financial organizations are facing tremendous shifts in their business models, regulatory requirements, and the competitive landscape. Undoubtedly, it is always a key priority for CIO and CTO is to reduce the infrastructure CAPEX and OPEX. In this “NSX-T based DMZ Rack Design for Banking” blog, let’s look at how NSX improves DMZ environment for banking
It is apparent that the server virtualization helped companies to reduce the infrastructure cost very much. furthermore, IDC estimated that NSX enhanced server utilization by approximately 20%. And it had its greatest impact on emissions reduction. Lesser emissions reduction resulted from the potential displacement of top-of-rack switches, physical firewalls, and other network and security devices. For the most part, it addresses the PCI compliance and segmentation use cases which is crucial in banking. Off-course I am not discounting, the fact that you need other functions such as DDoS, MFA, and deception to protect workloads outside of NSX-T
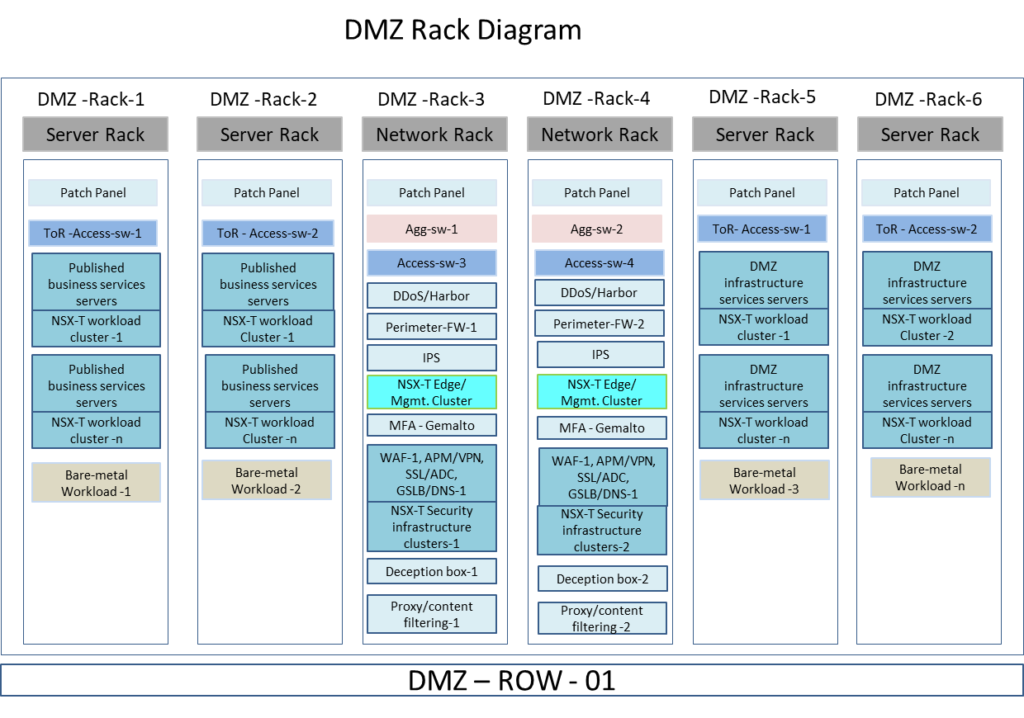
Rack HA and Resiliency
Before we delve into NSX-T specific advantage, let’s look at it from physical HA and resiliency perspective. Importantly, the data center requires careful planning to provide for efficient use of space, scalability, and ease of maintenance. It’s important to plan where to put the DMZ equipment. Above all, proper placement and planning allow for easy growth. The topologies shown above take a modular, platform-based approach to scale up or down as required within/ between the racks.
Finally, there are two models when it comes to access/switching environment 1) ToR ) and 2) EoR. Considering ToR design reduces cabling congestion which enhances the flexibility of deployment and installation, it is the model seen usually in a banking environment. Also, it is better to have a separate row dedicated specially for DMZ rack units.
Hosted Solutions HA and Resiliency
Now, let’s think about the hosted solutions generic design considerations. As design best practice, all computing resources should incorporate resilient network, power, and storage resources. The design should ensure redundancy across and within the hosted physical appliances includes an IPS, DDoS, Deception BoX, Perimeter FW, and Proxy. which include redundant power connections, power supply unit, and fan modules within the physical layer infrastructure.
Following are the physical HA and redundancy consideration for the each of the solutions hosted in DMZ environment
- Solution hosted on physical appliances will have a minimum of two instances working in an active-standby model
- The physical node pairs will be hosted in a separate rack to ensure FT in case of failure
- The virtual solutions part of the “infrastructure or business” server clusters will have active and standby instances on different racks
NSX-T specific design considerations
NSX helps in eliminating the need for physical appliances for firewalling (as a result of distributed firewalling and micro-segmentation) and for load-balancing/ADC functionality. Consequently, it is not only improving server utilization and thus improving power efficiency.
The above rack diagram shows the placement of each of NSX-T management and edge clusters within multiple and separate rack hardware infrastructures. It is worth noting that with NSX-T 3.0 you could have a completely independent NSX controller instance hosted for DMZ and internal network. This allows complete physical segregation and using federation to manage the policies across multiple domains. Furthermore, splitting up into separate rack designs creates separate failure domains for the server and management/edge clusters. As a result, failure in one domain does not impact the other domain and each block can be independent of each other as well.
Summary
The banking DMZ environment usually is loaded with a huge number of security solutions. And still may not address many of the PCI compliance requirements such as micro-segmentation. It is important to see how you can take advantage of NSX-T to reduce the overall infrastructure cost.
In conclusion, today’s data centers consume a lot of electricity. Conversely, with the NSX-T based design, it brings lots of efficiency in terms of saving on space, power, and cooling to the rack design. Furthermore, it effectively addressing banking compliance & security needs. In turn, the overall reduced power consumption delivered by infrastructure virtualization results in lower carbon emissions
I would also encourage you to read my related blog post on the subject ” Software Defined & Traditional Network” – Happy leaning