NSX-T Series: Part 10 – NSX-T Routing
In this “NSX-T Series: Part 10 – NSX-T Routing” part, we will discuss the types of routing in NSX-T and difference between DR and SR concepts.
As well as the methods of deploying EDGE in NSX-T.
But if you want to start from beginning you can refer my previous part of the Series:
NSX-T Series : Part 1 -Architecture and Deploy
NSX-T Series : Part 2 – Adding Compute Manager
NSX-T Series : Part 3 – Planning NSX VXLAN
NSX-T Series : Part 4 – Transport Zones and Use cases for Multi-Transport Zone
NSX-T Series: Part 5 – NSX-T N-VDS and VDS 7.0
NSX-T Series: Part 6 – NSX-T Uplink Profile
NSX-T Series: Part 7 – NSX-T ESXi Transport Node
NSX-T Series: Part 8 – NSX-T Logical Switching Use Cases
NSX-T Series: Part 9 – NSX-T Logical Switching Services
Gateway aka Logical Router
It is very important to understand the definition very properly because there has been architecture difference coming from NSX-V to NSX-T.
In simple language gateways are routers which enables routing feature from one IP subnet to another subnet. This definition remains same but little bit tweaked as per NSX infra.
We are aware in Data Center it is very important to provide optimal way routing East West traffic and same is being provided by NSX-T Gateway and Logical Routing.
Gateway provides features of peering with external routers which can be peered with BGP routing or static routing.
Gateway also gives features of Edge Firewall, NAT, Load Balancer, VPN and many more features.
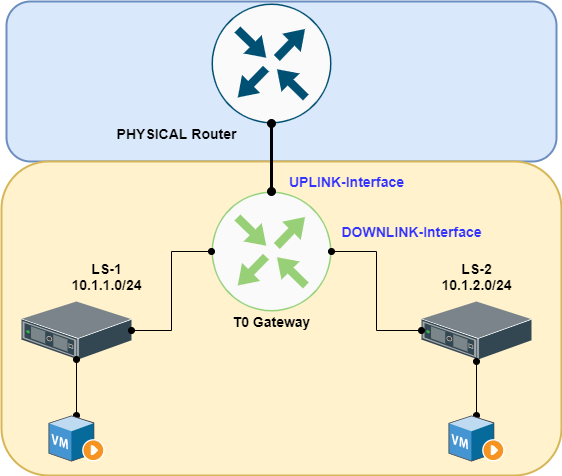
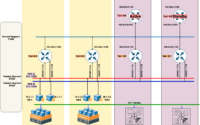
Service vs. Distributed Routing ( SR vs. DR )
When NSX-T was introduced the major confusing topics was SR and DR for many engineers, but to cut short it is very simple which we will discuss by difference table:
Distributed Routing ( DR )
- It runs locally in the transport nodes participating in the NSX fabric
- Typically runs as kernel module in the hypervisor
- Provides distributed East-West Routing
- Traffic between different subnet on same ESXi doesn’t leave hypervisor
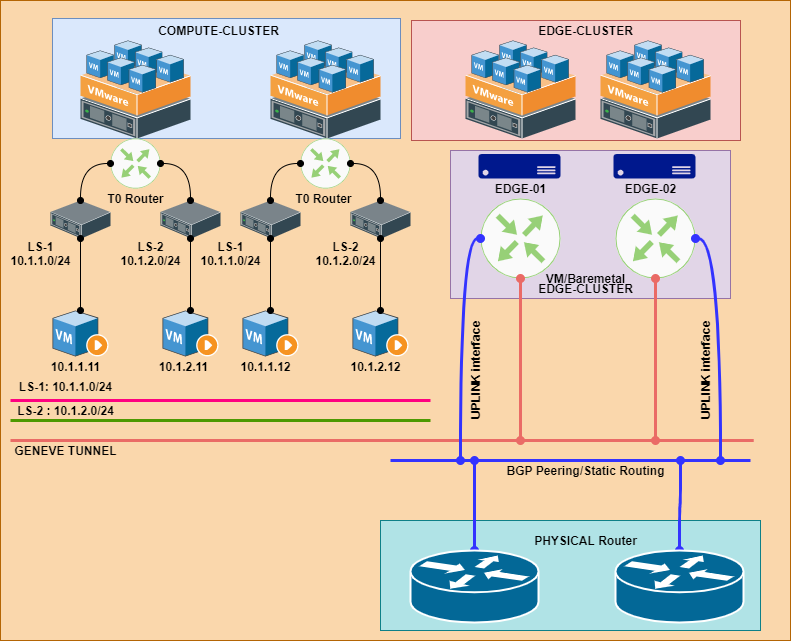
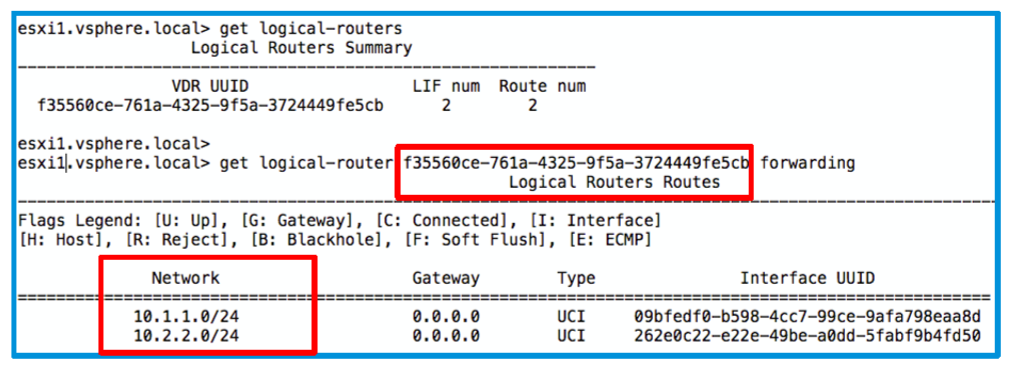
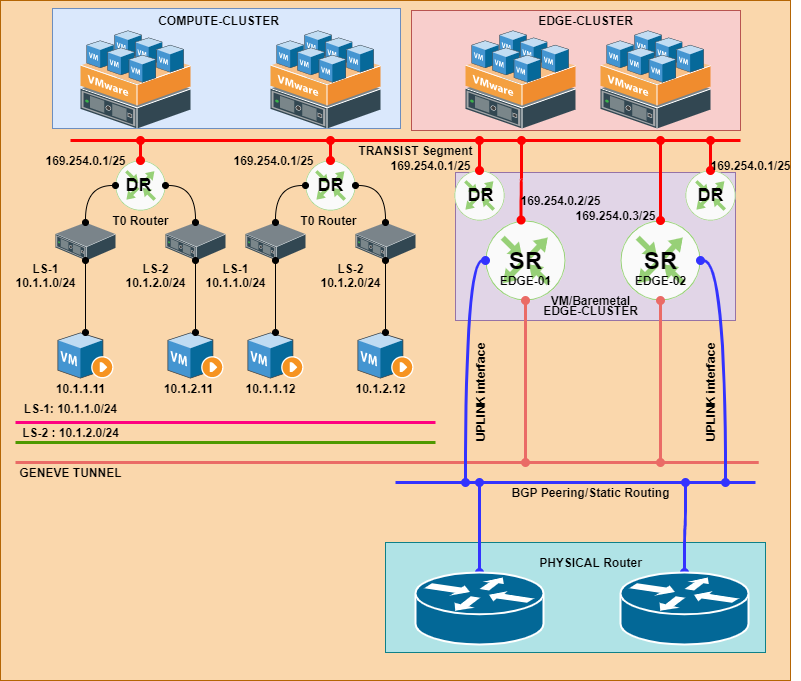
Service Routing ( SR )
- It provides on/off ramp gateway services including North-South Routing
- Provides centralized services like NAT, BGP, Edge Firewall, LB etc.
- The SR is initialized as a service on appliance on EDGE Node.
Bare Metal Edge Vs. VM Form Factor Edge
NSX-T gives flexible option of deploying EDGE which could be on now deployed on Certified Bare Metal servers which gives better performance. This gives more option to service provider and Telco players to use NSX-T in major of their use cases. There are some difference which is discussed below. For updated information please follow VMware Document.
Bare Metal EDGE Node
- Higher Thoughput : 35 Gbps
- Faster Convergence : sub second
- Specific/Certified NIC : Intel i40e, Mellanox, CX-4/5
- Rack & Stack
- High Service Scale
VM Form Factor EDGE Node
- Throughput : 20 Gbps
- Convergence: 1.5+ seconds
- No NIC requirements: VMXNET3 driver required
- Flexible deployment
- Services scale varies by the VM size
Summary
In this blog, we will discussed the types of routing in NSX-T and difference between DR and SR concepts. As well as the methods of deploying EDGE in NSX-T which could be baremetal of VM form factor. In next blog we will discuss more about Multi-Tier Routing and the difference between T0 and T1 gateway. Thanks for visiting blogs Happy Learning !


Very Informative article about DR & SR.
Keep continue…